The question “Does iPhone have a 3D camera?” is common among tech enthusiasts. Apple integrates advanced camera systems, but does it support true 3D depth camera data? While iPhones capture depth information, they lack a dedicated 3D element camera like some specialized devices.
Users sometimes notice 3D element camera weird glitches, especially in certain applications. Additionally, some report 3D element camera weird lines at the bottom of their images. For those needing a bullet camera holder 3D print, options exist to enhance imaging setups. Understanding the capabilities of iPhones helps users explore 3D imaging possibilities effectively.
What Is a 3D Camera?

A 3D camera captures depth and spatial information, creating lifelike, immersive images and videos. Unlike traditional cameras, it uses advanced technology like Cube Eye S100D – ToF 3D depth camera for precise depth mapping. These cameras are widely used in augmented reality, facial recognition, and 3D scanning applications.
Modern cameras often combine a sub-pixel camera with a perspective camera 3D to enhance image accuracy. This technology improves object detection and scene reconstruction. Whether for industrial or personal use, 3D imaging continues to evolve.
Accessories like a VBOX camera holder 3D print and 3D printed camera slider enhance camera stability and functionality. These tools help photographers and developers capture smooth, high-quality 3D visuals.
Who Invented the 3D Camera?
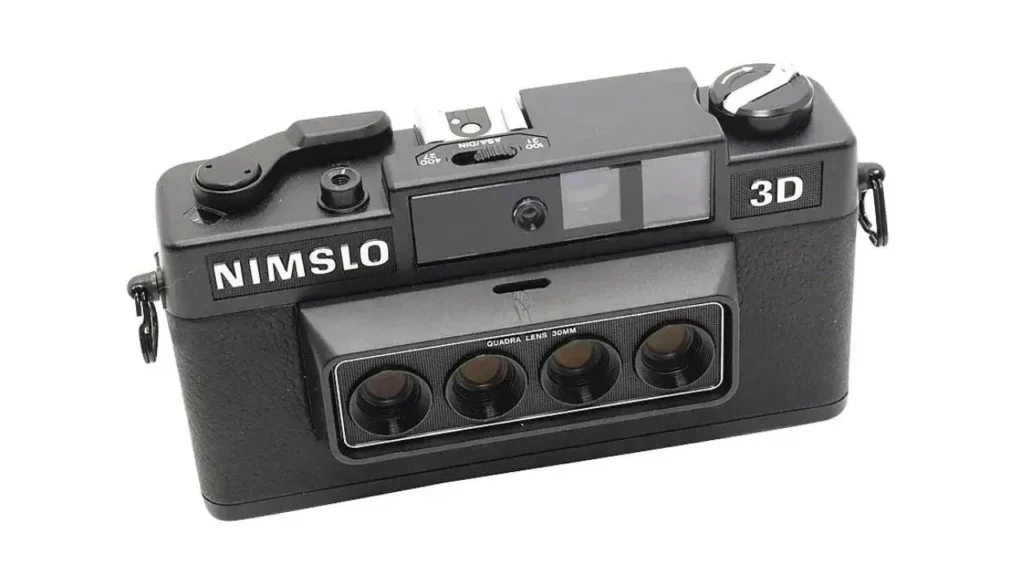
The invention of the 3D camera dates back to the 19th century when Sir Charles Wheatstone introduced the concept of stereoscopy. His research led to the development of the first camera in 3D, allowing images to have depth and realism. Later advancements improved this technology, leading to modern autostereoscopic 3D cameras that don’t require special glasses.
Today, the best 3D cameras offer incredible depth perception and high-quality imaging. These innovations paved the way for the 3D camera phone, enabling users to capture immersive visuals. Companies continuously refine 3D imaging to enhance photography, filmmaking, and augmented reality experiences.
Filmmakers and designers also utilize camera trackers in After Effects for seamless motion tracking. This technology improves animations and special effects, making digital content more lifelike. With ongoing advancements, cameras continue to evolve, shaping the future of imaging and interactive media.
How 3d Camera Works
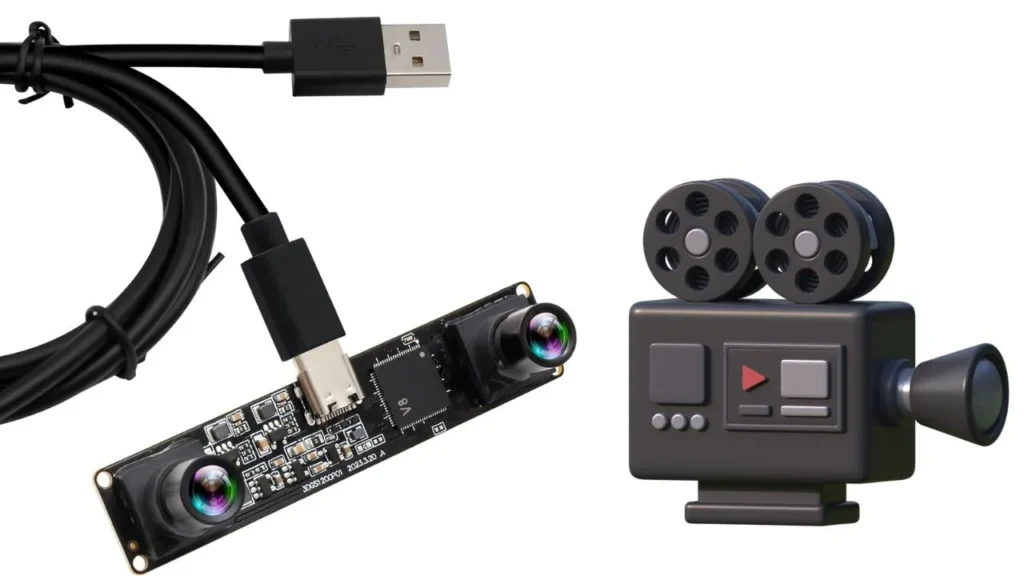

A 3D camera captures depth by using multiple lenses or sensors to mimic human vision. This technology enables a camera in 3D to measure distances and create immersive images. Advanced models, like an autostereoscopic 3D camera, display depth without special glasses.
Modern cameras rely on structured light, stereo vision, or time-of-flight methods. Some enthusiasts build custom 3D printed cameras for experimental photography. A 3D printer camera helps monitor prints for accuracy and precision.
In gaming, a camera following player in Unity 3D enhances realism. Understanding how 3D imaging works improves applications in photography, gaming, and printing.
Does iPhone Have a 3D Camera?
Many users wonder, Does iPhone have a 3D camera? While Apple devices feature advanced depth-sensing technology, they lack a true 3D camera 360. iPhones use LiDAR for improved depth mapping, but they don’t function as full 3D cameras for cars or VR applications.
Some apps offer 3D camera download options, simulating 3D effects using dual-lens cameras. However, these lack the precision of a dedicated 3D camera icon system. If Apple integrates this in future models, it may impact the 3D camera price in the market. For now, iPhones offer enhanced depth photography but not full 3D imaging.
How to use 3d camera

A camera captures depth and dimension, enhancing photography and videography. Understanding its features ensures the best results for immersive and high-quality 3D images.
1. Understanding 3D Cameras
A camera records images with depth, creating realistic visuals. Unlike standard cameras, they capture multiple angles for a layered effect. Autostereoscopic cameras allow 3D viewing without special glasses, making them popular in various industries. Whether using a 3D printed camera or a commercial device, knowing its capabilities is essential. Many professionals also use 3D camera PNG formats for digital design and editing.
2. Setting Up Your 3D Camera
Proper setup ensures the best 3D imaging experience. First, position the camera in 3D mode if available. Adjust settings for optimal lighting and depth perception. A 3D printer camera is useful for monitoring prints, while regular 3D cameras work for photography. Some devices offer built-in stabilization, preventing motion blur in complex shots.
3. Capturing 3D Images and Videos
To take high-quality camera shots, ensure proper focus and framing. Keep the camera stable to avoid distortions in depth perception. Many devices save files as 3D camera PNG images for post-processing. Professional setups use autostereoscopic cameras to create lifelike visuals without needing 3D glasses.
4. Editing and Enhancing 3D Media
Editing enhances the depth and clarity of cameras’ output. Software allows adjustments to color, contrast, and perspective. Many applications support camera in 3D mode for real-time adjustments. Designers often work with 3D printed camera models to achieve precise renderings. Professional editors prefer formats like 3D camera PNG for layering effects.
5. Using 3D Cameras for Different Applications
Cameras are widely used in filmmaking, gaming, and engineering. In film production, they create immersive scenes with deep visual effects. Engineers rely on 3D printer cameras to monitor detailed prints in real time. Even digital artists use autostereoscopic 3D cameras to design interactive content.
6. Troubleshooting Common 3D Camera Issues
Even the best cameras can have issues, but simple fixes exist. If images appear distorted, check focus settings and lens alignment. A 3D printed camera may need recalibration to function properly. When exporting files, ensure the 3D camera PNG format is compatible with editing software.
Read More: HOW TO CHANGE EXPOSURE ANDROID CAMERA?
How Much Are 3D Cameras?

The cost of a camera depends on features, quality, and purpose. Basic models start at a few hundred dollars, while professional 3D cameras for real estate can cost thousands. High-end options provide superior depth mapping and advanced imaging for various industries.
For gaming developers, a camera following player Unity 3D setup requires a compatible camera. Some users create custom mounts using 2007 Yamaha R6 mirror block off plates camera 3D print solutions. Additionally, certain software, like 3D camera DLL for SimCity 4 Mac, relies on specialized hardware for enhanced performance.
Choosing the right camera depends on your budget and specific needs. Entry-level models work for casual use, while premium cameras offer professional-grade results. Whether for real estate, gaming, or filmmaking, investing in the right camera ensures high-quality depth imaging.
How Much Does a 3D Camera Cost?
The price of a 3D camera varies based on features, quality, and brand. Basic models start at a few hundred dollars, while professional 3D film cameras can cost thousands. If you need a 3D video camera for filmmaking, expect higher prices due to advanced technology.
Custom options, like a Yamaha R6 camera 3D print file, allow users to modify mounting solutions. Professionals working with ZBrush camera focal length 3D printers need precision, which affects costs. Investing in a high-quality camera ensures better depth, resolution, and compatibility for various creative and industrial applications.
Choosing the right 3D camera depends on budget and intended use. Whether for filmmaking, 3D modeling, or custom printing, costs vary widely. Understanding your needs helps balance price and performance for the best value.
How to Create a 3D Camera in After Effects

Creating a 3D camera in After Effects enhances motion graphics, adding depth and realism. This feature is essential for animations, simulations, and 3D video camera projects. Many professionals use it for advertising, 3D film camera effects, and architectural visuals.
To start, enable the camera for real estate by activating After Effects’ 3D layer. Adjust the ZBrush camera focal length 3D printer settings for precise perspective. Customizing the depth, focus, and movement refines your scene. After Effects also supports importing Yamaha R6 camera 3D print files for advanced visualizations.
Animating the camera requires keyframes for smooth transitions and realistic movement. Use depth of field to enhance focus, mimicking a 3D film camera. Experimenting with angles and lighting improves the final output. Whether for real estate or cinematic projects, mastering After Effects’ 3D video camera tools creates immersive experiences.
What iPhone Has a 3D Camera?
Many users ask, What iPhone has a 3D camera? While no iPhone includes a true camera, some models feature advanced depth-sensing technology. Apple’s LiDAR scanner enhances depth perception, improving augmented reality and portrait photography. However, it does not function as a fully dedicated camera for stereoscopic imaging.
The latest iPhones use LiDAR and multiple lenses to simulate 3D camera effects. These features improve depth mapping, making them useful for AR applications and creative photography. Although Apple hasn’t introduced a standalone 3D camera, their technology continues advancing toward immersive imaging experiences.
Future iPhone models may include a real camera with enhanced depth features. Apple constantly improves camera technology, pushing boundaries in mobile photography. Users can expect innovations that bring camera capabilities closer to reality in upcoming releases.
What Is a 3D Camera in Mobile?

A camera in mobile devices captures depth and spatial details for realistic imaging. Unlike regular cameras, it uses advanced sensors to measure distances and create 3D effects. Many smartphones integrate 3D cameras for enhanced photography, AR applications, and facial recognition technology.
These cameras use LiDAR or time-of-flight sensors to generate accurate depth maps. This technology improves portrait mode, AR gaming, and security features like facial unlocking. Some devices also support 3D scanning, allowing users to create digital 3D models. The evolution of cameras enhances smartphone capabilities for both creative and practical uses.
With a 3D camera, users experience more immersive visuals and interactive applications. Whether for photography, augmented reality, or gaming, this technology is transforming mobile imaging. As smartphone manufacturers continue innovation, future cameras will likely offer even more advanced features.
FAQ’s
How to Move Camera in Paint 3D?
To move the camera in Paint 3D, use the Orbit, Pan, or Zoom tools. Click and drag to rotate, adjust the view, and position objects in a 3D space.
What Is 3D Camera Tracking?
Camera tracking analyzes video footage to track movement and depth. It helps integrate 3D objects seamlessly into real-world environments for filmmaking, AR, and VFX applications.
What Is a 3D Depth Camera?
A 3D depth camera measures distance using infrared or LiDAR technology. It enhances AR experiences, facial recognition, and depth-based photography in smartphones, security systems, and industrial applications.
Do Camera and Lenses See in 3D?
Standard cameras capture 2D images, but stereoscopic cameras mimic human vision for 3D depth perception. Dual-lens setups enable realistic depth effects and improved spatial awareness in photography and video.
Do 3D Cameras Exist?
Yes, cameras exist and capture depth for realistic imaging and augmented reality. They are used in smartphones, filmmaking, medical imaging, and gaming for immersive and interactive experiences.
How Can I Take 3D Photos?
To take 3D photos, use a camera, dual-lens smartphone, or dedicated app. Capture from different angles, then combine images to create a depth-rich 3D effect.
Conclusion
In Conclusion, The 3D camera has revolutionized imaging, bringing depth and realism to various applications. While iPhones feature advanced depth-sensing, they still lack a true camera for full stereoscopic capture. However, Apple’s LiDAR technology enhances photography, AR, and facial recognition.
As mobile technology advances, future iPhones may integrate dedicated cameras for immersive visuals. Until then, users can explore third-party apps and accessories to simulate 3D effects. Whether for filmmaking, gaming, or photography, the demand for camera innovations continues to grow. The future promises even more advanced depth-sensing capabilities for mobile devices.